This article provides an in-depth analysis of the service life of rolling stock in the railway system of Uzbekistan — in particular, the service life of freight and passenger cars, their technical condition, and the degree of wear and tear. Based on the analysis, it was established that a large part of the existing wagon fleet has exceeded the standard service life and is becoming unusable. The article also substantiates the need to apply deterministic and probabilistic approaches to the modernization of the wagon fleet and the assessment of service life. Based on global experience and practical research, strategic proposals have been developed for the development of wagon repair infrastructure, the introduction of technological innovations, and the renewal of service-expired rolling stock.
Keywords: rolling stock, service life, technical condition, wagon fleet, depreciation rate, railway transport, forecasting, modernization, operational indicators, repair infrastructure, deterministic approach, probability model, freight transportation.
Freight transportation volume growth and ensuring train traffic safety are strategic priorities. Achieving these goals requires the use of modern, reliable, and technically advanced rolling stock. However, the aging wagon fleet and increasing technical failures present serious challenges. Therefore, developing a scientifically grounded forecast of the operational fleet is essential for effective modernization and renewal of the rolling stock.
In recent years, negative incidents in rail transport have led to a decrease in the volume of freight transported by rolling stock. As a result, a large portion of the wagon fleet became redundant, the purchase of rolling stock was virtually halted, and simultaneously, the freight wagon fleet shrank due to the expiration of service life. In the context of steady growth dynamics in transportation volume, a shortage of certain types of rolling stock has become apparent. This has forced specialists to pay serious attention to the active part of production assets — freight wagons, which currently have an average service life of 15–20 years. The technically aging wagon fleet will not be able to meet future demand for cargo transportation. This may lead to customers abandoning railway transport services, switching to other modes of transport, and consequently, resulting in a loss of revenue for the country's railway system.
In 1992, at the 5th meeting on railway transport, the freight car fleet of the Ministry of Railways of the former USSR was distributed among the railway administrations. Since the distribution, the freight car fleet has decreased by more than 40 % [6–10]. This decrease was mainly due to the removal from inventory due to technical conditions. At the time of the distribution of the wagon fleet, the average age of the inventory fleet was 15.3 years, and now this figure has reached 24 years.
Table 1
Analysis of the inventory fleet of wagons as of 01.01.2024
|
Wagon type |
Average service life, years |
Service life, years |
Depreciation amount |
Number of wagons with an expired service life |
|
Closed cars |
28 |
32 |
82,4 |
34,2 |
|
Platforms |
29 |
32 |
80,2 |
39,9 |
|
Gondola cars |
17 |
22 |
75,2 |
41,3 |
|
Tankers |
26 |
32 |
80,8 |
41,4 |
|
Passenger cars |
25 |
26 |
86,5 |
49 |
|
Total |
25 |
28.8 |
81,2 |
41,36 |
According to Table 1, as of January 1, 2024, 41.36 % of the inventory fleet of wagons have exceeded their standard service life. The average service life across all wagon types is 25 years, while the average standard service life is 28.8 years. The overall depreciation amount of the wagon fleet is 81.2 %. Among the types, passenger cars have the highest share of expired service life wagons at 49 %, and gondola cars and tankers also show significant aging with 41.3 % and 41.4 %, respectively. This indicates an urgent need for fleet renewal, especially for wagons carrying aggressive cargo, as their technical condition poses higher risks [1–3].
This part of the wagon freight fleet is the rarest, since more than 80 % of the total volume of transportation is carried out by wagons of this type. Obsolete and worn-out rolling stock does not allow for the transition to modern transportation technologies, increasing inter-repair intervals, the warranty mileage of trains, increasing their weight, reducing emissions into the atmosphere, and solving many other problems related to time and traffic safety requirements.
Analysis of world experience and author's research have shown that the problem of maintaining the wagon fleet and improving its technical condition should be solved, first of all, by improving the quality of capital and depot repairs of wagons by introducing new materials and technologies for their processing, as well as by mastering capital restoration repairs with an increase in the service life of parts. In this regard, the application of a scientifically based approach to the creation of an effective strategy for the development of the railway wagon fleet, its own repair base, and the production of rolling stock elements is of great importance.
Within the scope of the conducted research, the study of production capabilities revealed that a deterministic approach is primarily employed in calculations. This approach is based on processing data from previous years' cargo loading volumes, as well as specific indicators of wagon utilization:
Np = UƟ (1)
Here: U — working time, wagons/day;
Ɵ — wagon turnover, days.
Modern research approaches are characterized by the probabilistic and correlational nature of operational processes, rather than their unambiguous determination. Methods developed based on this approach serve to increase the effectiveness of decision-making, especially in developing strategic programs for modernizing railway car fleets and improving wagon repair infrastructure in rail transport. Conducted studies have shown that to obtain the most accurate forecast for the working fleet, it is necessary to consider the influence of numerous external and internal factors that determine its quantitative state. In this formulation of the problem, it is essential to account for the impact of indicators such as freight turnover, section speed, train weight, turnaround time, static load, average daily productivity, and idle time during freight operations and at technical stations.
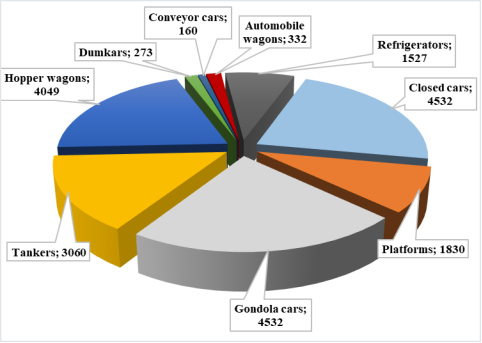
Fig. 1. Number of wagons operated by JSC «Uzbekistan Railways» (data as of 2024)
In this regard, the implementation of the following strategic measures is relevant:
– Wide implementation of models based on probabilistic and statistical methods in assessing the technical condition and service life of rolling stock;
– Development of investment programs and mobilization of financial resources for the phased replacement of wagons with expired service life with new ones;
– Development of technologies for the modernization of repair infrastructure, especially for major repairs and extending the service life of parts;
– Increasing the level of localization of wagon production and developing innovative solutions using new, modern materials;
– Continuously conducting scientific and practical research in collaboration with JSC «Uzbekistan Railways» and implementing the findings into practice.
Furthermore, the overall efficiency of the railway system can be significantly enhanced through the scientific forecasting of wagon service life, comprehensive assessment of component conditions, and analysis of operational indicators. Such an approach not only yields economic benefits but also contributes to improved safety, environmental sustainability, and the international competitiveness of railway transport.
The results of an in-depth study of the service life and technical condition of rolling stock in the railway system reveal that a substantial portion of existing freight and passenger cars have reached a critical level of depreciation and exceeded their standard service life. This situation adversely affects not only the quality and safety of transportation but also the overall economic efficiency of the railway system. Therefore, it is essential to determine the service life and forecast the condition of the operational fleet through the application of modern scientific methods, particularly probabilistic and analytical modeling techniques.
In this regard, modernizing the rolling stock, replacing outdated wagons, strengthening repair infrastructure, and implementing technologies that extend service life are among the most pressing issues in the sector. It is impossible to envision sustainable development of railway transport without long-term and scientifically grounded approaches.
References:
- Akhmedov M., Tuxtamuradov A. Fundamentals of the Development of Logistics Systems in Railway Transport. — Tashkent: TDTU Publishing House, 2021. — 180 p.
- Qayumov N. H. Methods of Ensuring Traffic Safety in Railway Transport. — Tashkent: Ilm ziyo, 2020. — 154 p.
- Khasanbaev H. Analysis of the technical condition and service life of freight wagons. — Scientific article, «Transport Journal» 2023, № 2. — pp. 33–41.
- Ministry of Transport of the Republic of Uzbekistan. Statistical reports on railway transport. — Tashkent, 2023.

