Epistemology in training and research processes is central from its starting point and theoretical determination, justification, and guarantee. Currently, with the development of intelligent systems and their adaptation in the daily life of human and natural processes, it demands overcoming contradictions from the postmodern approach to more balanced and comprehensive proposals such as those that exist from complexity theory.
Keywords : epistemology, postmodern, complexity theory, intelligent systems.
Introduction
Methodology in scientific research is defined based on the epistemological approach that determines the approach with which phenomena are to be understood from different areas for the construction of new knowledge and the understanding of existing knowledge. This is related to the results of these research processes, hypothesis construction, and their confirmation.
The accelerated advancement of technologies and intelligent systems poses a significant challenge in understanding the process of constructing that knowledge, its variables, and difficulties. What is the starting point proposed to understand these processes? What research is being conducted in this regard? This article is important because it opens up the possibility of addressing these questions from an exploratory perspective.
Therefore, these questions and clarifications of epistemological approaches, the state of their academic and scientific production on these topics, become highly relevant in the training processes of new technologies and their implications in society's life and the future of their development.
Research Objective
To conduct a bibliometric search and critical analysis regarding the tensions existing in epistemology from the postmodern approach to complexity theory as an approach to intelligent systems.
Method
Bibliometric analysis is a fundamental methodology for analyzing research, originating in the field of library science and information science, providing an overview of the research field at a given time [1].
Taking into account the terms related to the topic of the present article of analysis and reflection regarding the tensions arising between the postmodernist approach, the positivist vision, and complexity theory to address the phenomena that correspond to science, a list of basic words (in English) was created for the bibliographic review process. The words were processed through a thesaurus, which provides the possibility of the correct semantic relationship for the search equation construction process to be effective.
Through the words presented and a relationship through operators and Boolean logic, the search equation was formulated.
Table 1
Key Words
|
Basic words |
|
From the related terms of the basic words that make up the core of the review and reflection in the present article, the following logical relationships with Boolean operators were projected and tested in the Scopus database for the advanced search:
Table 2
Equation and keyword ratio table.
|
Terms |
Equation |
|
Epistemology; Epistemological |
(«epistemology» OR «epistemological») |
|
Complex thought; Complexity; Complexity theory; Transcomplexity |
(«complex thought» OR «complexity» OR «complexity theory» OR «transcomplexity») |
|
Postmodernism; Positivism; Neo-Positivism |
(«postmodernism " OR «positivism»); («neo» AND «positivism») |
|
Intelligent System; AI; Artificial Intelligent; Robotic |
(«intelligent» OR «system») AND («AI» OR «artificial intelligent» OR «robotic*") |
In this regard, the logical relationship was delimited and executed beforehand in the Scopus search engine, ultimately generating a complete and delimited equation.
Boolean equation:
TITLE-ABS-KEY ((«epistemology» OR «epistemological») OR («complex thought» OR «complexity» OR «complexity theory» OR «transcomplexity») AND («postmodernism " OR «positivism») AND ((«intelligent» AND «system») OR («AI» OR «artificial intelligent» OR «robotic*")) OR («neo» AND «positivism»)).
Through this advanced search option, the aforementioned equation was executed, limiting the retrieved works to the topic of interest of the present article. The graphs from the data processing in the Scopus database were extracted, and subsequently, documentary review and analysis were conducted as a research technique. This research technique is understood as a series of techniques and methods aimed at locating, processing, and storing information in documents as a first stage, followed by the systematic, coherent, and reasoned presentation in a new document as a second stage [2]
Bibliometric Analysis
The results of the search and bibliometric analysis revealed a finding of 59 documents conducted and published in the Scopus database.
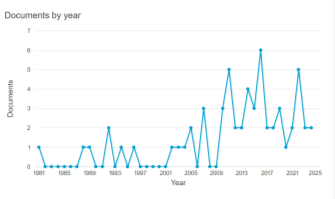
Fig. 1. Documents by year. Source: Scopus (2024)
In the previous graph, it can be observed that the production and publication of works related to epistemic approaches between postmodernism and complexity theory are from the year 2009 to 2022, covering a range of 13 years during which academic and scientific production worldwide addressed these topics.
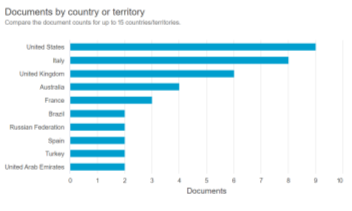
Fig. 2. Document by country or territory. Source: Scopus (2024).
The main countries with the highest production in the framework of the topic are the United States of America with 9 relevant works in the database, Italy with 8 works, and finally the United Kingdom with 6 works.
Results and Discussion
The territory of epistemology has been of great interest to philosophers, where it can be approached from personal perspectives [3], as a philosophical view of science. In this sense, epistemology has had central concepts, theories, and problems around understanding knowledge and its justification with terms of its own such as 'evidence' and 'guarantee' [4].
Currently, it can be understood that the prefix 'post' in postmodern approaches, as the most recent designation with which it can be designated and at the same time acquires new relevance, is the situation of crisis that has prevailed in many of the investigative approaches and readings of reality in Western thought throughout the twentieth century [5]. Here is where the techno-scientific and sociopolitical progressivism that could illuminate the preceding centuries entered into crisis [5].
That postmodernism, which from the phrase 'The end of the great narratives' could not respond to the great situations of complexity that the world was experiencing, but on the other hand, generated a cultural and epistemic relativism, which affirms from its vision the existence of theoretical postulates (understanding that there are no 'naked facts', since they enter our knowledge and end up being purely theoretical), provides a view of the impossibility of objectivity [5].
This generated in the research processes great problems of inconsistency in epistemological approaches, which leads to taking postmodern criticism to its ultimate consequences, which generated a process of contradiction due to its own starting point in the annulment of the viability of any kind of “absolute truth”. In that process of postmodern criticism, a movement emerged that bet on overcoming those contradictions, in what the world would understand as the paradigm of complexity [5].
Therefore, it is important to understand that complex systems contain the complexity sciences that generically designate the explanatory models, theories, and concepts, with which it has been consolidating to address important phenomena in the social sciences [6]. Its foundation traverses important aspects such as non-linearity, self-organization, emergence, dissipation, instabilities, fluctuations, evolution, sudden, irreversible, and surprising changes [6].
In this sense, understanding intelligent systems due to the constant evolution that this technology is experiencing is of great importance. The concept of intelligent systems emerges as a type of system derived from different and successive applications of artificial intelligence [7]. Therefore, in the digital age, computer tools have been created to automate tasks that require mental effort; the capabilities of these tools have had a growing progressivity, requiring more and more intelligence to perform tasks; this whole process has generated intelligent systems [7].
According to Priogine (1997), «we witness the emergence of a science that is not limited to simplified, idealized situations, but rather places us in front of the complexity of the real world» [5, p. 6]. With this, Priogine (1997) makes it clear that there is evidence of a science that allows human creativity to be manifested as the singular expression of a fundamental common trait experienced at all levels of nature [5].
With this, it is relevant to emphasize equally the role of systemic thinking as the way to abstract and consolidate the possibility of apprehending the real world through the science of complexity and complex thinking itself. About this, physicist Fritjof Capra (1998) mentions that the great shock that 20th-century science has had was the realization that systems could no longer be addressed solely through analysis; in this way, it is understood that these types of approaches must be made from the organization of the whole, concentrating not on the basic components but on the essential principles of organization [5]. Capra states that systemic thinking is «contextual», as opposed to analytical; in this way, being analysis the process of isolating something to study and understand it, systemic thinking is the representation of framing that something that is desired to be studied within the context of a higher whole [5].
With this, complex thinking seeks to set aside the plots and problems of knowledge, identifying the synchronous similarities of the scientific trends of existing disciplines that are commonly fostered from individuality [8]. With this, the field of complexity sciences is nourished by perspectives that come from both the natural sciences and the human and social sciences, the latter being derived mainly from postmodernist thought [8].
Finally, trying to conciliate and take the most pertinent aspects of the approaches, based on the vision of sociologist Rigoberto Lanz, a proposal is framed that tries to reasonably approach the intentions of postmodernism when addressing social phenomena, taking into account its methodological flaws, and rigorously supporting an alternative vision that takes the positive contributions of postmodernism, as well as the contributions of complexity [9].
The concept of transcomplexity has as such a connection between the emergence of a postmodern episteme (as another way of thinking) and different options of complex thinking [9]. Those connections in themselves have repercussions in the methodological field, in those conceptual and categorical elaborations [9].
Conclusions
Different proposals from the postmodern approach made in the 20th century for scientific research are currently being questioned due to their different difficulties and contradictions that tendentiously relativize methodological processes and the results that can be obtained in the research of social and human sciences.
Now that the world is in a constant technological evolution and a close relationship between personal and social development with the advancement of 4.0 revolution technologies, complexity theory or complexity sciences come to have a relevant role in as much as they propose reference points that take intersections relationships between different elements or sets of elements as complex; thus providing a greater understanding of how different phenomena that may have an impact on different areas in human, social, and natural life should be approached.
References:
- Merigó, J., & Yang, J. (2017). A bibliometric analysis of operations research and management science. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omega.2016.12.004
- Martinez-Corona, J., Palacios-Almón, G., & Oliva-Garza, D. (2023). Guía para la revisión y el análisis documental: propuesta desde el enfoque investigativo. RA XIMHAI, Vol. 19, núm. 1.
- Kofer, B. (2001). Personal Epistemology Research: Implications for Learning and Teaching. Journal of Educational Psychology Review. Vol. 13, No, 4. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1023/a:1011965830686
- Audi, R. (2010). Epistemology: A contemporary introduction to the Theory of Knowledge. Routledge, New York. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203846469
- Caro, A. (2002). El paradigm a de la complejidad como salida de la crisis de la posmodernidad. Revista Discurso, órgano de la Federación Andaluza de Semiótica, n° 16–17, 2002. Universidad Complutense de Madrid.
- Maldonado, C. (2011). Termodinámica y Complejidad: Una introducción para las ciencias sociales y Humanas . Ciencia y Sociedad. Ediciones desde abajo.
- Molina, M. (2022). What is an intelligent system? Dept. of Artificial Intelligent, Universidad Politécnica de Madrid.
- Silva-Rodríguez, A. (2015). Racionalidad, Posmodernidad, Complejidad e Ivestigación Científica: Nuestro Rumbo . Revista Digital Internacional de Psicología y Ciencia Social. Vol, 1. Num. 2.
- Chirinos, S. (2007). Complejidad y Postmodernidad. Revista Moñongo. No. 29, Vol. XV, Julio — Diciembre.

